Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, stiffness, and eventually joint damage. It can also affect other parts of the body, leading to systemic complications. In this blog, we will know the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle management strategies for rheumatoid arthritis, shedding light on this often-misunderstood condition.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the body’s own tissues, primarily the synovium the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This results in inflammation, which can lead to joint damage, deformity, and disability over time. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear on the joints, RA is driven by an autoimmune response.

Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms can vary from person to person and may fluctuate in intensity over time. Common symptoms include:
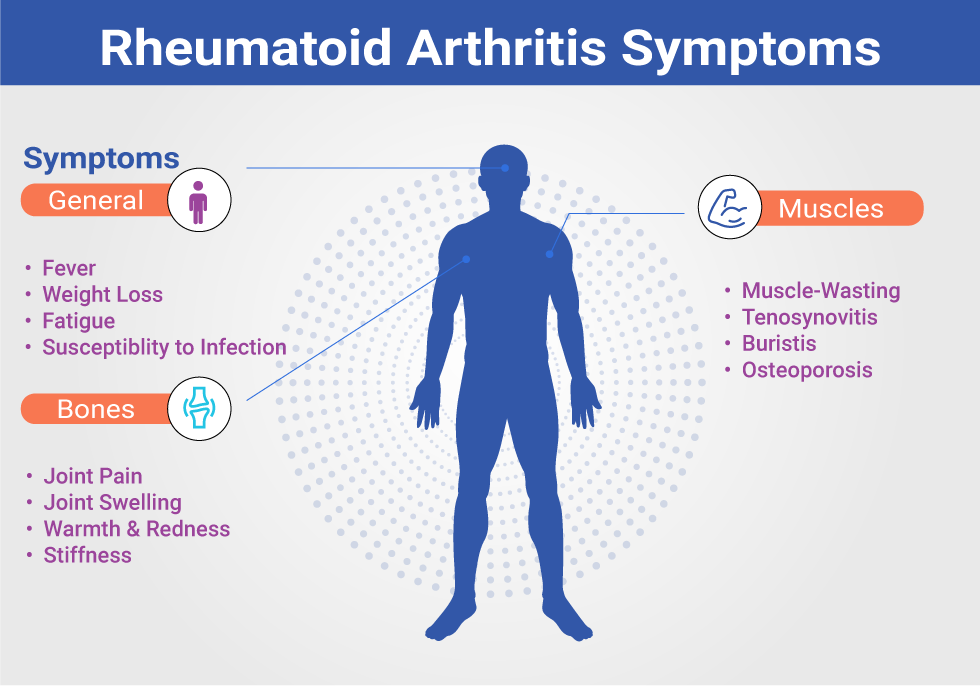
- Joint Pain: This is the most common symptom, typically characterized by a dull ache or tenderness in the affected joints. The pain often feels worse upon waking (morning stiffness) and may improve with activity.
- Joint Stiffness: Stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity, is another classic symptom. The stiffness can last for 30 minutes or more and may improve with movement.
- Joint Swelling: Inflammation in the joints can cause swelling, making the affected joints appear puffy or enlarged. This swelling is often symmetrical, meaning it affects both sides of the body in similar ways.
- Warmth in Joints: Inflamed joints may feel warm to the touch due to increased blood flow to the area.
- Fatigue: People with RA often experience persistent fatigue and tiredness, even after getting enough sleep.
- Loss of Function: As the disease progresses, joint damage can lead to a decreased range of motion and difficulty performing daily activities.
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
While the precise cause remains uncertain, it is thought to be the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal influences.
- Genetic predisposition: Individuals with a family history of rheumatoid arthritis are at higher risk of developing the condition, suggesting a genetic component.
- Environmental triggers: Certain environmental factors, such as smoking, infections, and exposure to pollutants, may trigger the onset of rheumatoid arthritis in genetically susceptible individuals.
- Abnormal immune response: Rheumatoid arthritis is primarily an autoimmune disease, characterized by the immune system attacking healthy tissues. It is thought that an abnormal immune response triggered by genetic and environmental factors leads to the inflammation observed in RA.
How Rheumatoid Arthritis is Diagnosed
Early diagnosis of RA is essential for effective management and preventing joint damage. A comprehensive evaluation by a rheumatologist is necessary, and diagnostic tests commonly used may include:
- Physical examination: A thorough examination of the joints, looking for signs of inflammation, swelling, and tenderness.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation and autoimmunity, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and rheumatoid factor (RF). Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are also commonly measured and are highly specific to RA
- Imaging studies: X-rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help assess joint damage and monitor disease progression.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Once diagnosed, the goals of treatment for RA are to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, prevent joint damage, and improve overall function and quality of life. Treatment strategies may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents are commonly used to manage its symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy and occupational therapy can help improve joint function, flexibility, and strength while teaching adaptive techniques for managing daily activities.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress can all help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being in people with RA.
- Surgery: In severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis where joint damage is extensive, surgical interventions such as joint replacement surgery may be necessary to restore function and relieve pain.
lifestyle changes that can help with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Diet: Eat a balanced and anti-inflammatory diet, Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. These foods are rich in antioxidants and nutrients that can help reduce inflammation.
- Exercise: Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining joint flexibility, reducing stiffness, and strengthening muscles that support the joints. Activities like walking, swimming, and yoga are gentle on the joints but offer significant benefits.
- Weight Management: Excess weight puts extra strain on your joints and can worsen RA symptoms. Aim for a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night. Adequate sleep helps reduce inflammation and promotes overall well-being.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for RA and can worsen symptoms. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your overall health.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation can help manage pain and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis poses significant challenges, but with the right approach, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Understanding the disease, seeking early diagnosis, and adhering to personalized
treatment plans are crucial steps. Additionally, incorporating healthy lifestyle habits and regular exercise can further support symptom management. It’s essential to acknowledge the invaluable contributions of orthopedic doctor like Dr. Hardik Padhiyar. Whose expertise and dedication play a pivotal role in guiding patients through their journey with rheumatoid arthritis. By working closely with knowledgeable and compassionate healthcare providers, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can navigate the complexities of their condition and strive for optimal health and well-being.






