Arthritis, a term echoing through medical corridors, encompasses various joint disorders affecting millions globally. This scientific exploration unravels the intricacies of arthritis, ranging from its etiology to effective management, ensuring a well-rounded understanding for a pain-free life.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Arthritis?
Arthritis, derived from Greek roots, translates to “joint inflammation.” It’s not a singular disease but a collective term for over 100 types of joint disorders. The most prevalent types include osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), each with distinct characteristics and underlying mechanisms.
Etiology and Risk Factors
Genetic Predisposition:
A family history of arthritis elevates susceptibility, indicating a genetic component. Certain gene variants may increase the likelihood of developing specific types of arthritis.
Age and Gender:
Aging is a significant risk factor for arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, exhibits a higher incidence in women. The interplay between aging and gender underscores the complexity of arthritis’s origins.
Environmental Factors:
Beyond genetics, environmental factors contribute to arthritis development. Exposure to certain pollutants, infections, or occupational hazards may trigger the onset of arthritis in susceptible individuals.
Pathophysiology of Arthritis
Inflammation:
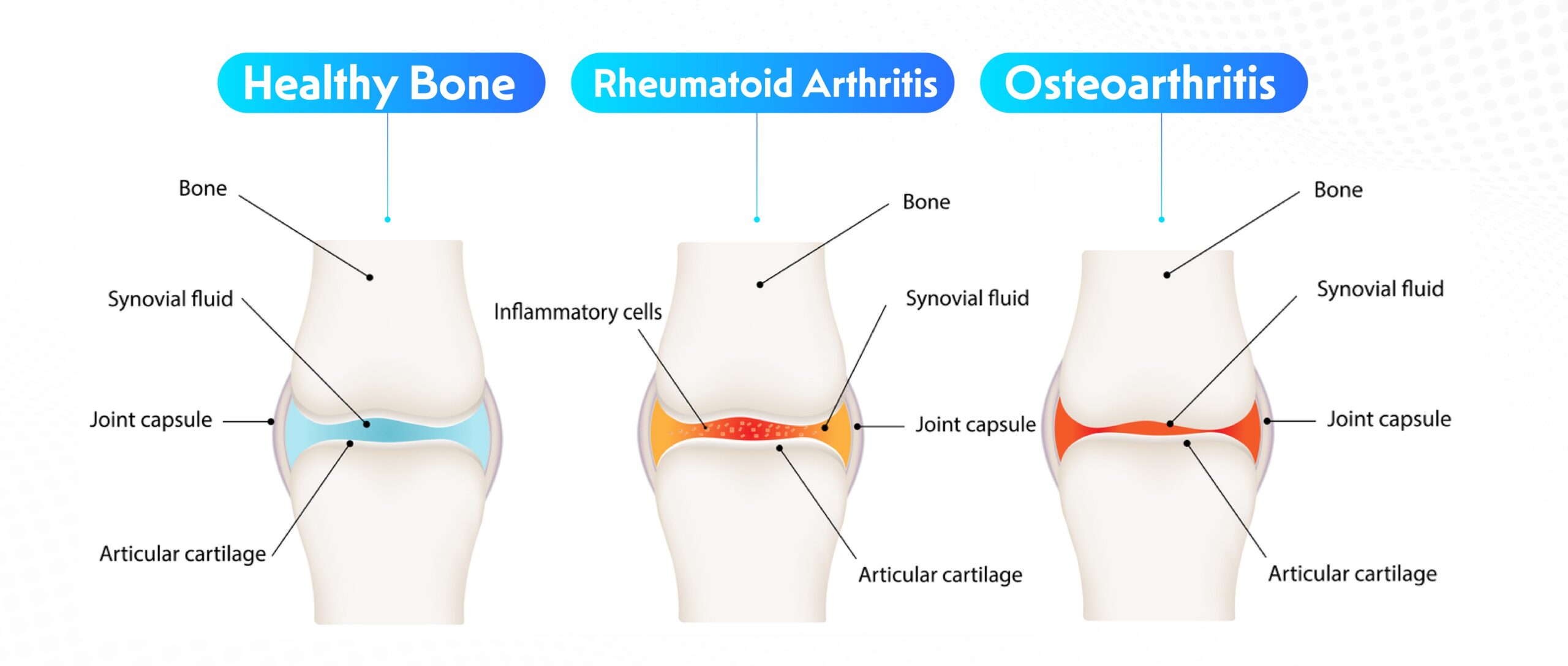
At the core of arthritis lies inflammation. The immune system, designed to protect the body, misfires, attacking healthy joint tissues. In rheumatoid arthritis, the synovium—the lining of the membranes surrounding joints—becomes the battleground for an autoimmune assault.
Cartilage Degeneration:
Osteoarthritis, the most common type, is characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage—the protective tissue covering joint ends. This degeneration results in pain, swelling, and limited joint mobility.
Arthritis Symptoms

Joint Pain:
Arthritis manifests primarily as joint pain, ranging from a dull ache to intense discomfort. Understanding the nature and pattern of pain is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Swelling and Redness:
Inflammation triggers visible swelling and redness around affected joints, often accompanied by a sensation of warmth.
Morning Stiffness:
Many arthritis sufferers experience morning stiffness, a pervasive tightness that can last for hours and impede the initiation of daily activities.
Types of Arthritis
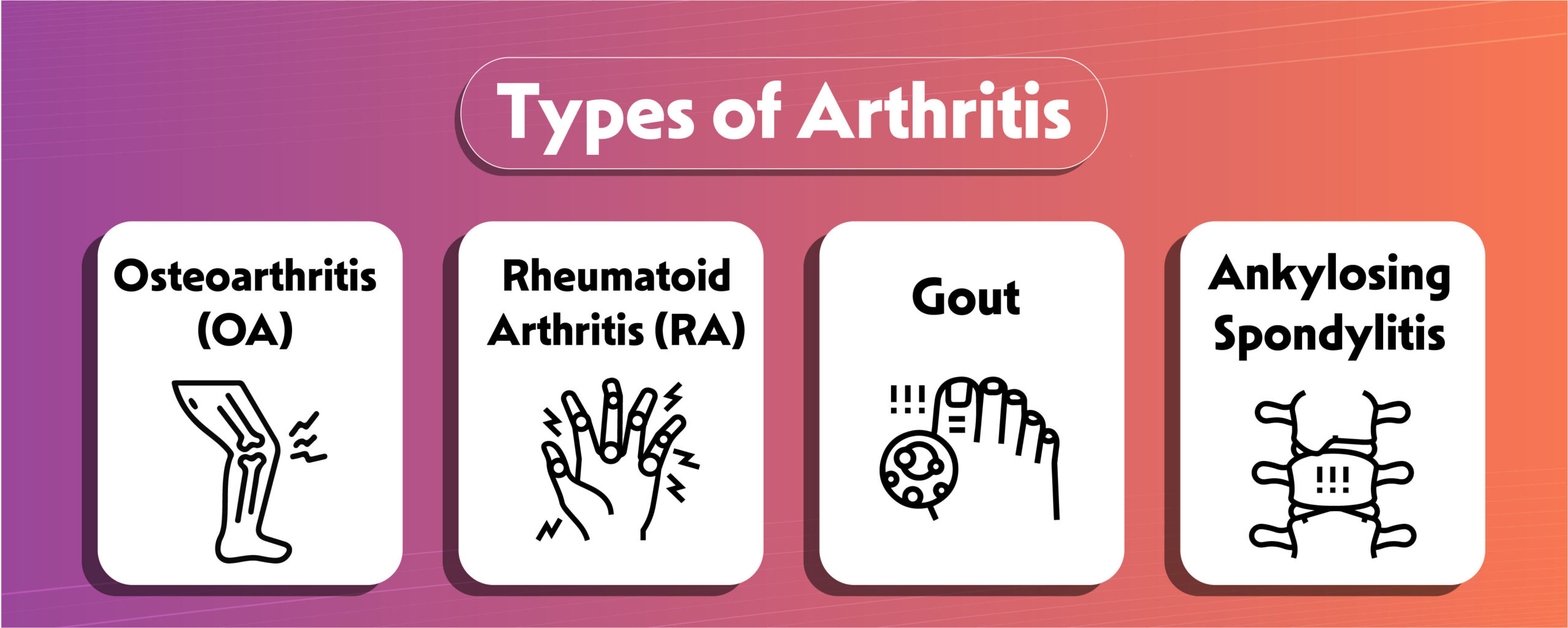
Osteoarthritis (OA):
Commonly associated with aging and wear-and-tear, OA affects the hips, hands, spine and knee pain. It gradually erodes cartilage, leading to joint pain and stiffness.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
An autoimmune disorder, RA targets the synovium, causing inflammation. This chronic inflammation can result in joint deformity and damage.
Gout:
Characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, gout leads to sudden and severe attacks of pain, often affecting the big toe.
Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Primarily impacting the spine, this type of arthritis causes inflammation and stiffness in the vertebrae, potentially leading to fusion.
Arthritis Disease Causes
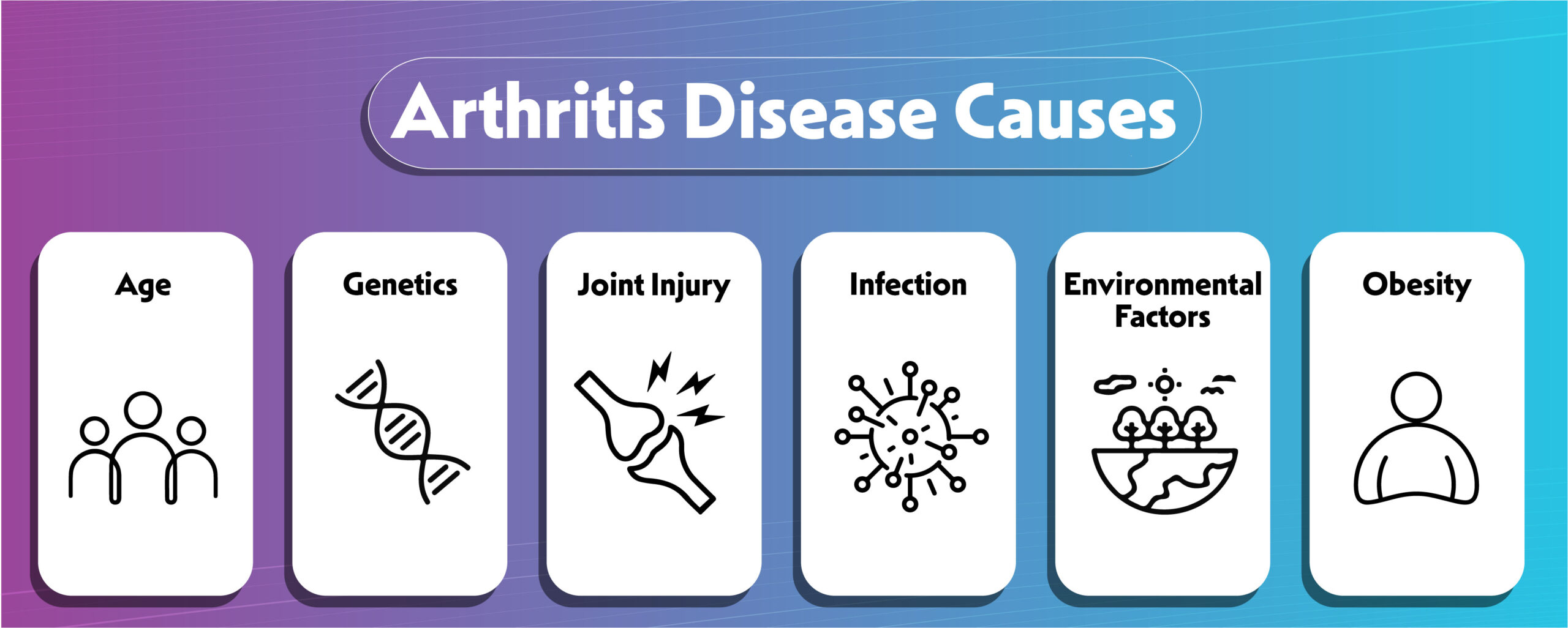
Genetic Factors:
Specific genes linked to arthritis susceptibility highlight the hereditary component. Genetic testing may offer insights into an individual’s predisposition.
Age and Gender:
Aging contributes to joint wear-and-tear, particularly in weight-bearing joints. The hormonal and immune system differences between genders also play a role in arthritis development.
Environmental Triggers:
Exposure to environmental factors such as smoking, pollution, or infections can trigger or exacerbate arthritis, especially in genetically predisposed individuals.
Arthritis Diagnosis and Tests
Physical Examination:
A thorough examination by an orthopedic doctor involves assessing joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. Observation of symptoms plays a vital role in diagnosis.
Imaging Studies:
X-rays, MRI, and CT scans provide detailed images, revealing joint abnormalities, cartilage loss, and bone damage.
Blood Tests:
Specific blood markers, including rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies, aid in diagnosing autoimmune arthritis.
Surgical Interventions for Arthritis
Arthroscopy:
This minimally invasive procedure allows the visualization and treatment of joint problems. Arthroscopy Surgery can be particularly beneficial for conditions like torn cartilage.
Joint Replacement:
In severe cases of arthritis, joint replacement surgery becomes a viable option. This involves replacing damaged joints, most commonly the hips or knees, with artificial components.
Arthritis Management and Treatment
Medication:
Anti-inflammatory drugs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and pain relievers are prescribed to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Weight management is crucial for reducing stress on weight-bearing joints. Adaptive tools and ergonomic adjustments can ease daily activities.
Physical Therapy:
Tailored exercises and physical therapy programs help maintain joint flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and improve overall function.
Strategies for Pain-Free Living with Arthritis
Healthy Diet:
Consuming an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help manage arthritis symptoms.
Stress Management:
Stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can positively impact arthritis symptoms.
Regular Monitoring:
Regular check-ups with an Orthopedic surgeon, such as Dr. Hardik Padhiyar, ensure proactive management and adjustment of treatment plans.
Conclusion
In summary, staying attuned to your body’s signals is vital for a vibrant, active life. If you recognize signs of knee issues, particularly those linked to arthritis, consult with a best joint replacement surgeon promptly. Early intervention is key, and for personalized guidance, consider reaching out to Dr. Hardik Padhiyar. Your path to optimal knee health starts with informed care.