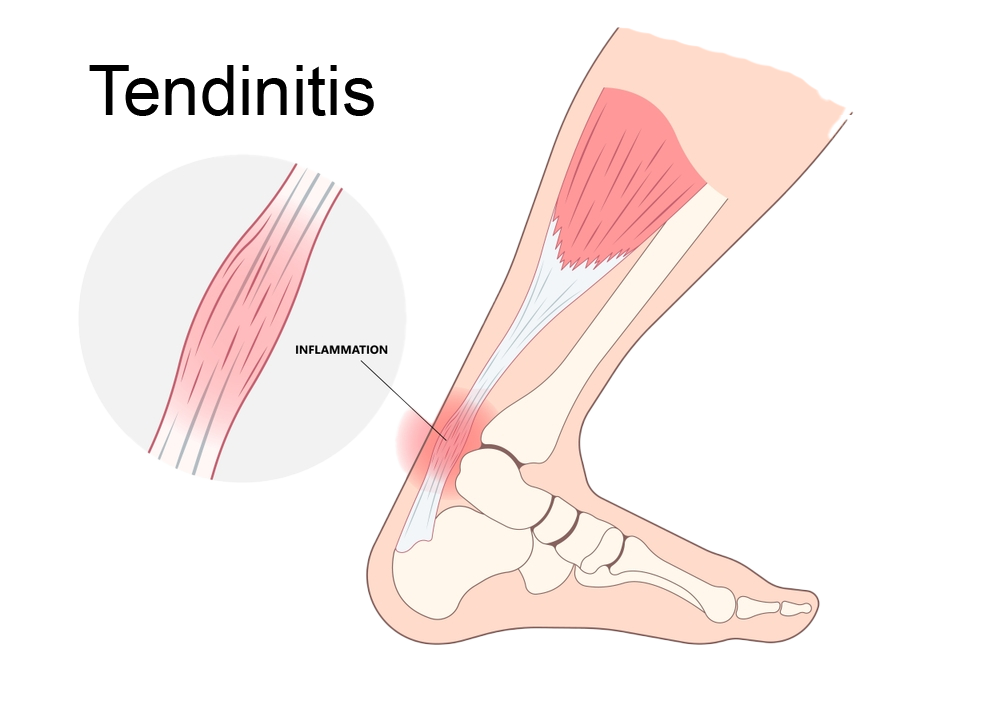
Tendinitis, a common musculoskeletal condition, affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the inflammation of tendons, the fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones.
What is Tendinitis?
Tendinitis, also known as tendonitis, is the inflammation of a tendon, resulting in pain and discomfort. Tendons play a crucial role in facilitating movement by transmitting the force generated by muscles to the bones. When these tendons become inflamed, it can lead to a range of symptoms and hinder normal daily activities.
Types of Tendinitis
- Rotator Cuff Tendinitis: Affecting the shoulder pain tendons, particularly the rotator cuff, this type is common among athletes and individuals engaged in repetitive overhead activities.
- Achilles Tendinitis: Occurring in the Achilles tendon at the back of the ankle, this type is often associated with overuse or sudden increases in physical activity.
- Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow: Tendinitis can also affect the tendons around the elbow, causing pain on the outer side (tennis elbow) or inner side (golfer’s elbow) of the joint.
- Patellar Tendinitis: Known as “jumper’s knee,” this type affects the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone and is prevalent among athletes involved in jumping sports.
Symptoms of Tendinitis
- Localised pain and tenderness around the affected tendon are hallmark symptoms of it
- Swelling and Warmth: Inflammation often leads to swelling and increased warmth in the affected area.
- Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion. Tendonitis can result in stiffness, making it challenging to move the joint through its full range of motion.
- Crepitus: Some individuals may experience a crackling or grating sensation when moving the affected joint.
Causes of Tendinitis
Several factors contribute to the development oftendonitis
- Overuse and Repetitive Movements: Engaging in repetitive activities or overusing a particular joint can strain the associated tendons. Leading to inflammation.
- Age and Wear-and-Tear: Tendons lose elasticity with age, making them more prone to injury. Wear-and-tear over time can contribute to the development of tendinitis.
- Poor Posture and Body Mechanics: Incorrect body mechanics and poor posture can put additional stress on tendons, increasing the risk of inflammation.
- Sports and Physical Activities: Participation in certain sports or activities that involve repetitive motions, such as running or playing tennis, can contribute to the development of tendinitis.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes, which involve inflammation, may predispose individuals to tendinitis.

Diagnosis and Treatment of Tendinitis
Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. Medical professionals may use a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRI) to diagnose tendinitis.
- Conservative Approaches: Initial treatment often involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy can help strengthen the affected tendons and improve range of motion.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to alleviate severe inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: In rare instances where conservative measures fail, surgical intervention may be considered to repair or remove damaged tendon tissue.
How to Prevent Tendinitis?
Preventing tendonitis involves adopting healthy lifestyle practices and making mindful choices in daily activities. Some preventive measures include:
- Proper Warm-Up and Stretching: Engage in proper warm-up routines and stretching exercises before participating in physical activities.
- Gradual Progression: Avoid sudden increases in the intensity or duration of physical activities, allowing the body to adapt gradually.
- Ergonomic Considerations: Maintain proper ergonomics at work and home to reduce strain on tendons.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises into your routine to build muscle and support tendon health.
Living with Tendinitis: Coping Strategies and Support
Living with tendonitis presents unique challenges, and adopting effective coping strategies is essential. To manage daily life with this condition, individuals can prioritise pain management through techniques like heat or ice therapy. Modify activities to reduce strain on affected tendons, and incorporate adequate rest and recovery periods. Engaging in physical therapy and practising proper body mechanics contribute to long-term well-being. Attention to psychological health, including mindfulness and counselling, helps address the emotional impact of chronic pain. Lifestyle adjustments, such as optimising ergonomics, maintaining a balanced diet, ensuring quality sleep, and fostering open communication with Orthopedic surgeon, play pivotal roles. Seeking support from healthcare teams, joining support groups, educating close contacts, and relying on emotional support from friends and family contribute to a holistic approach in navigating the challenges of living with it
Conclusion
When it comes to managing tendinitis and other orthopedic treatments, having the guidance of a skilled and compassionate orthopedic surgeon like Dr. Hardik Padhiyar can make all the difference. With his expertise and dedication to patient care. He provides comprehensive treatment options tailored to everyone’s needs. Helping them navigate the challenges of living with tendinitis and regain their quality of life. From accurate diagnosis to personalized treatment plans and ongoing support. He ensures that his patients receive the highest standard of care every step of the way. Trust in Dr. Hardik Padhiyar as your partner in orthopedic health and take the first step towards a pain-free and active lifestyle.